Ligand Binding to a Receptor Kinase Results in
4 What is a ligand biology quizlet. Increased kinase activity through autophosphorylation.

Tyrosine Kinase Receptors An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Activation of the intrinsic tyrosine.
/11614.png.aspx)
. Binding of tissue-type plasminogen activator or α 2-macroglobulin α 2 M to LRP1 resulted in Src family kinase SFK activation and SFK-dependent Trk receptor transactivation in PC12 cells and neurons. Binding of a ligand to a receptor changes its shape or activity allowing it to transmit a signal or directly produce a change inside of the cell In this section well look at different types of receptors and ligands seeing how they interact to turn information from outside the cell into a change inside the cell. All of these answer options are correct.
This indicates that the binding of signaling molecules to activated EGFRs results in. Phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic domain of the receptor. 8 What does a ligand look like.
Ligand binding to the extracellular domain results in receptor dimerization. Given that ligand binding is essential for the rapid internalization of epidermal growth factor receptor EGFR the events induced by ligand binding probably contribute to the regulation of EGFR internalization. Ligand binding to G-protein coupled receptors results in conversion of RhoA-GTP to RhoA-GDP.
Ligand-induced oligo- merization required tyrosine kinase activity and nine different tyrosine kinase substrate residues. 1 What Is A Ligand Biology. CHAPTER 9 1Ligand binding to a receptor kinase results in.
The canonical model of RTK endocytosis involves rapid internalization of an RTK activated by ligand binding at the cell surface and subsequent sorting of internalized ligand-RTK complexes to lysosomes for degradation. What is the end result of activation of the MAP kinase pathway. Ligand binding to the c-terminal ligand binding domain is an important regulatory event in ar function resulting in a conformational change that disrupts an intramolecular interaction between the amino terminus and the carboxy terminus initiates posttranslational modifications dissociates the ar from heat shock proteins hsps and results in.
Of the 90 unique tyrosine kinase genes identified in the human genome 58 encode receptor tyrosine kinase proteins. These events include receptor dimerization activation of intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity and autophosphorylation. A conformational change in the cytoplasmic domain of the receptor Ligand binding to a receptor kinase results in.
Cytokine and growth factor receptors are activated when the soluble growth factor binds and alters the protein-protein interactions between receptor components on the cell surface triggering intracellular receptor phosphorylation and downstream signaling. A change in gene expression resulting in cell division What causes the inactivation of a G protein. Binding of cytoplasmic signaling molecules.
Ligand binding to a receptor kinase results in. Endocytosis is the major regulator of signaling from receptor tyrosine kinases RTKs. Expert Answer When signaling molecules bind to RTKs they cause neighboring RTKs to associate with each other forming cross-linked dimers.
Ligand binding induced the formation of receptor oligomers which were found in both the plasma membrane and intracellular structures. Upon ligand binding bone morphogenetic protein BMP receptors form active tetrameric complexes comprised of two type I and two type II receptors which then transmit signals to SMAD proteins. View Test Prep - CHAPTER 9 from BIOLOGY 2107 at Georgia State University.
As signaling proceeds activated receptors will bind to phosphotyrosine-binding proteins such as actin Cbl and Grb2 resulting in the oligomerization of the EGFR. What mutation is commonly found in RAS genes in cancer cells. As a result the kinases phosphorylate each other to activate each other.
In contrast to SPR PWR examines anisotropic optical contents of receptor-ligand complexes and differentiates mass density changes from conformational changes 45. Trk receptor transactivation was necessary for activation of Akt and extracellular. How does ligand binding to a receptor tyrosine kinase result in the activation of RAS.
5 What is ligand in cell signaling. 9 What is ligand in botany. How does this mutation influence RAS activity.
6 Is ligand a receptor. 3 What is an example of a ligand in biology. Here we describe a signaling pathway whereby LRP1 transactivates Trk receptors.
The ligands bind to RTKs promoting RTK dimerization and in some cases oligomerization which brings the two kinase domains in close proximity. Receptor tyrosine kinases are the high-affinity cell surface receptors for many polypeptide growth factors cytokines and hormones. Ligand binding changes amplitude position and width of reflected lights.
7 What is ligand class 12. In PC12 cells and neurons binding of two structurally distinct ligands to LRP1 activated Src family kinases which then activated Trk receptors as measured by Trk receptor tyrosine phosphorylation the activity of two downstream kinases Akt and extracellular signalregulated kinase 1 and 2 and neurite outgrowth assays. However many receptors involve three or more cell surface components and the effect of this.
All of these choices are correct. Ligand binding induces a conformational change in the ectodomain leading to the reorientation of the intracellular kinase domains resulting in the activation of the asymmetric kinase dimer. 2 What is a ligand.
For RTKs ligands are generally small proteins between 50 and a few hundred amino acids long which are secreted by cells. Thus PWR can be applied to analyze the changes in receptor conformation and local mass density 46. Ligand binding to the receptor domain regulates the ratio of kinase to phosphatase activities of the signaling domain of the hybrid Escherichia coli transmembrane receptor Taz1 J Mol Biol.
Orthogonal ligand-protein pairs also known as re-engineered ligand-receptor interfaces or re-engineered enzyme-substrate interactions are a protein-ligand binding pair made to be independent of the original binding pairThis is done by taking a mutant protein naturally occurring or selectively engineered which is activated by a different ligand carefully. The two adjacent tyrosine kinase domains phosphorylate one another to tyrosine residues autophosphorylation. 10 Where are ligand.
RhoA-GTP dissociates from RhoA-GDPi allowing RhoA to bind downstream targets. Receptor tyrosine kinases have been shown not only to be key regulators of normal cellular processes but also to have a critical role.

Enzyme Linked Receptor An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Tyrosine Kinase Receptors An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Binding Initiates A Signaling Pathway Biology For Majors I

Cell Signaling By Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Cell

Camp Signal Pathways Ligand Binding To Various G Protein Coupled Download Scientific Diagram

Binding Of Single Mutant Epidermal Growth Factor Egf Ligands Alters The Stability Of The Egf Receptor Dimer And Promotes Growth Signaling Journal Of Biological Chemistry
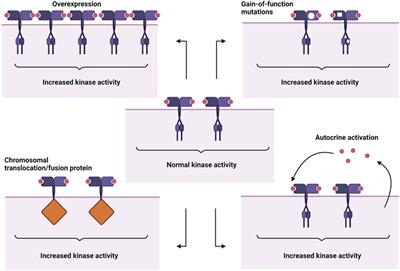
Frontiers Receptor Tyrosine Kinases And Their Signaling Pathways As Therapeutic Targets Of Curcumin In Cancer Pharmacology

Upon Ligand Binding Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Rtks Dimerize And Download Scientific Diagram

Signaling Receptors Biology For Majors I

Tyrosine Kinase Receptors An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Receptor Tyrosine Kinase An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Schematic Representation Of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase And Downstream Download Scientific Diagram
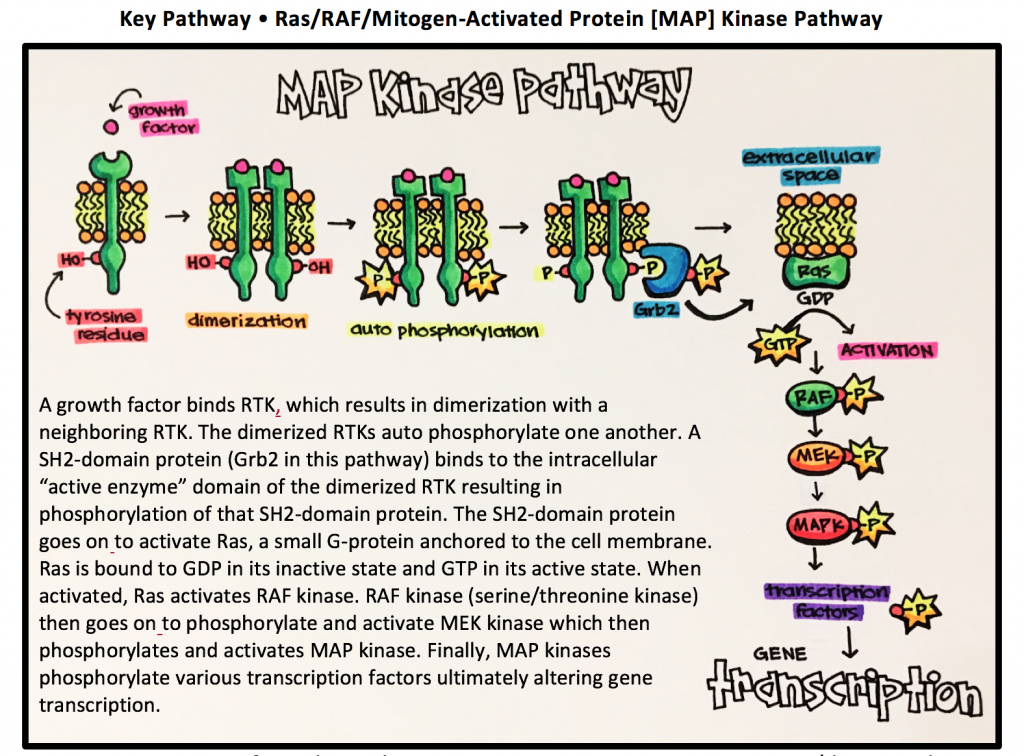
13 Enzyme Linked Receptors Principles Of Pharmacology Study Guide
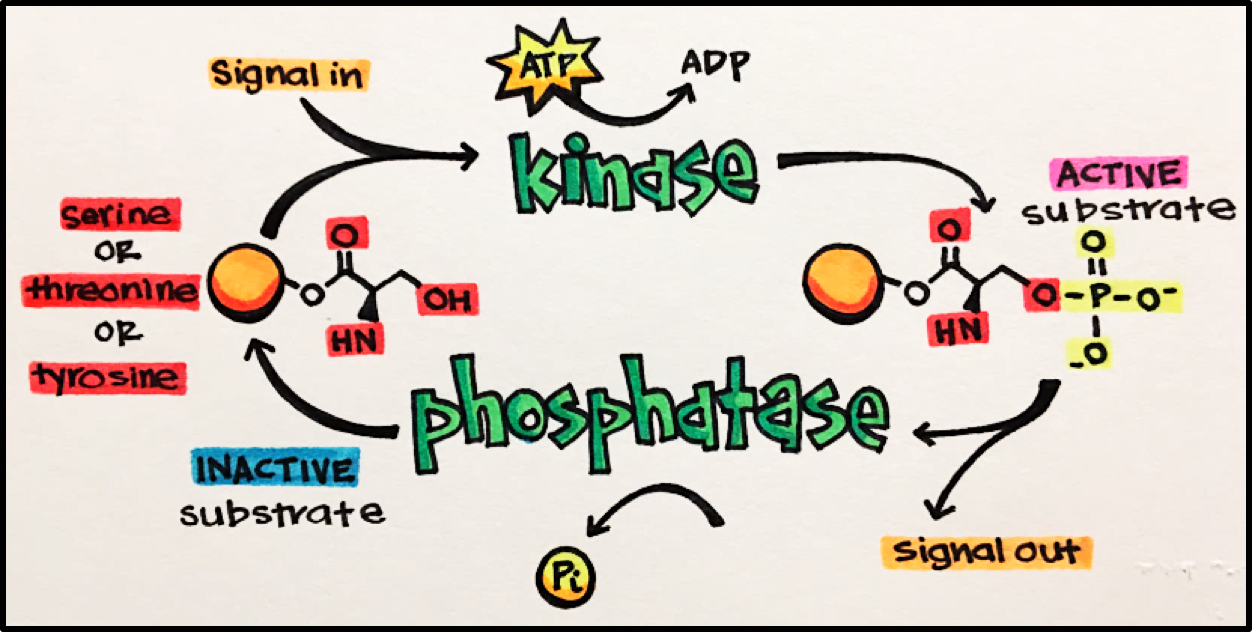
13 Enzyme Linked Receptors Principles Of Pharmacology Study Guide
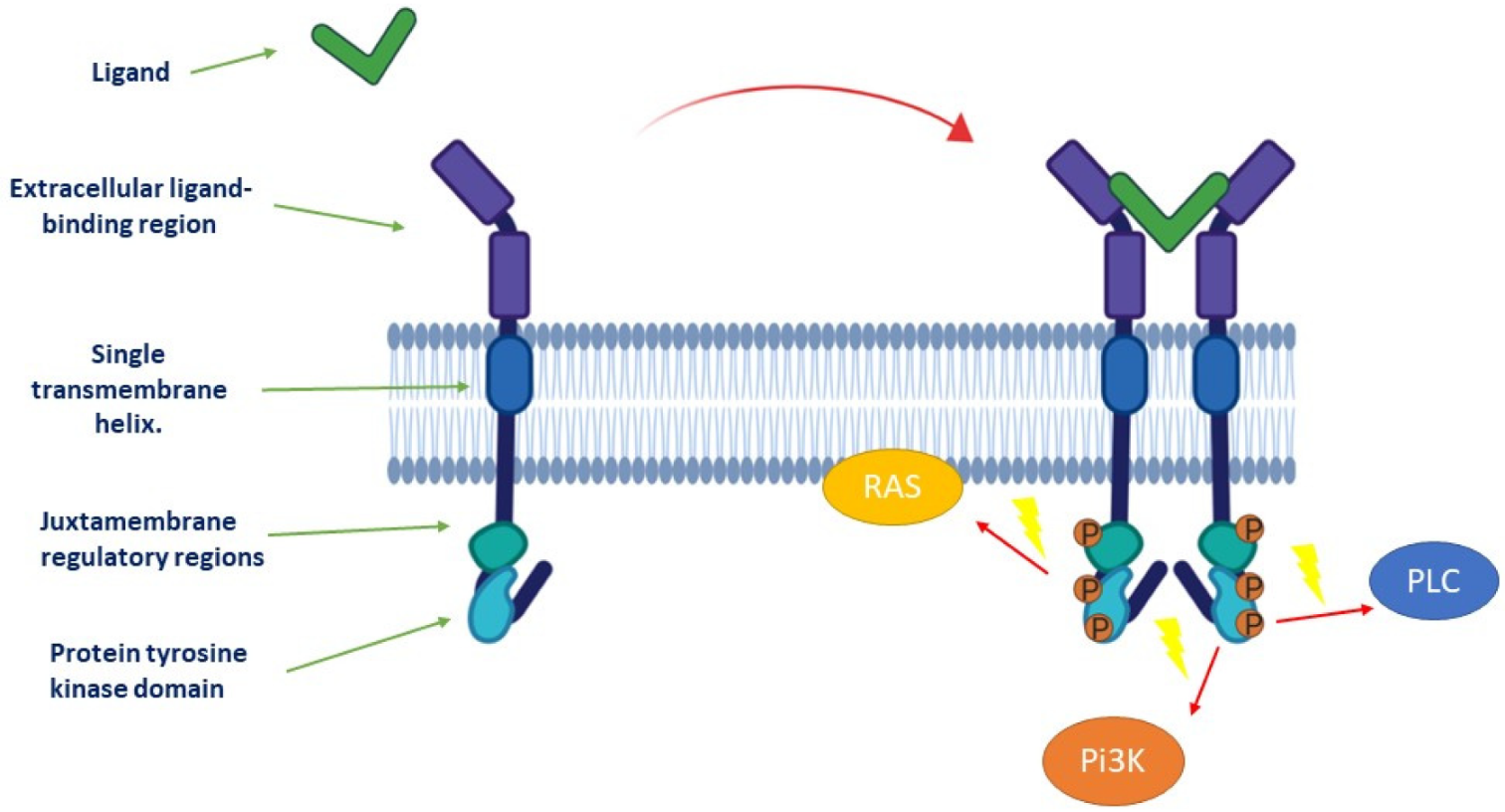
Cancers Free Full Text Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors In Cancer Breakthrough And Challenges Of Targeted Therapy Html
/11614.png.aspx)
Rtk Ctk Kinase Cell Based Assays

Upon Ligand Binding Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Rtks Dimerize And Download Scientific Diagram
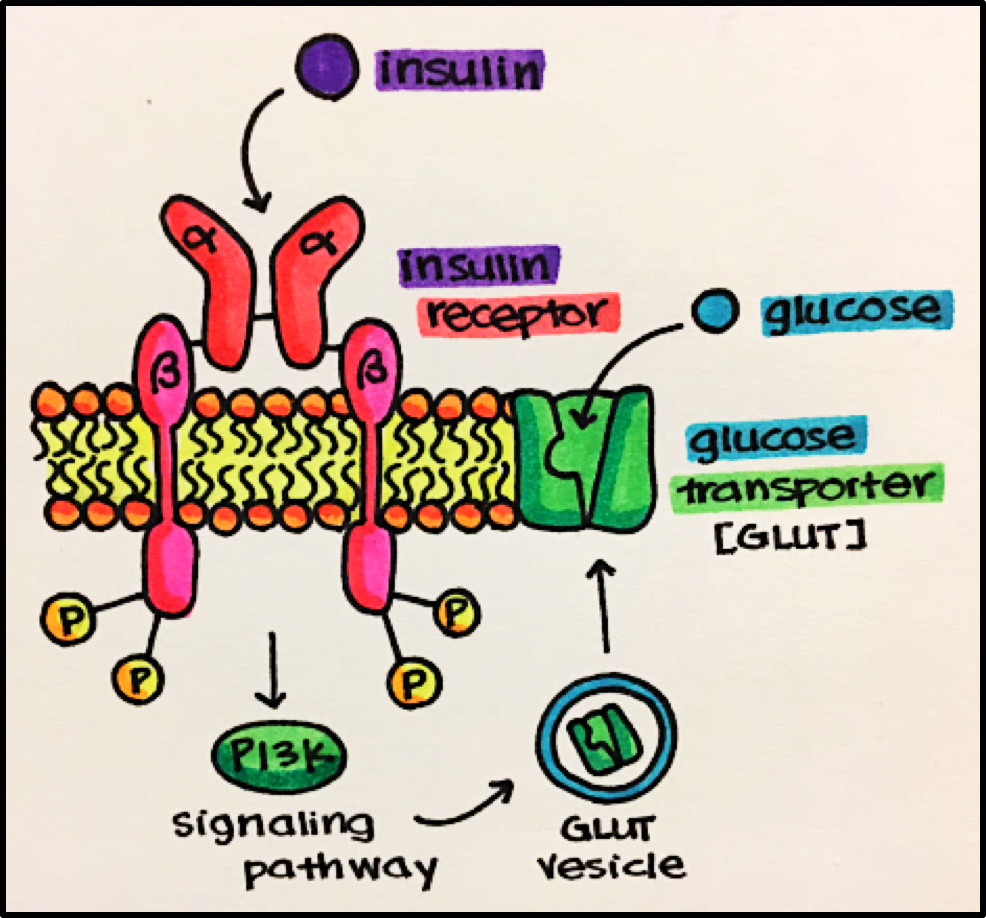
13 Enzyme Linked Receptors Principles Of Pharmacology Study Guide

Comments
Post a Comment